How to Calculate Tile for a Shower: A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide
Publish on: 28-Mar-2025

Tiling a shower can completely transform its look—but how do you know how many tiles to buy? Don’t worry—this guide makes it easy to figure out, even if you’ve never tiled before. We’ll walk you through a simple formula, step-by-step instructions, and tips for handling tricky spots like niches and corners. Let’s dive in!
Why You Should Calculate Shower Tiles First
Tiles are typically sold by the square foot, so knowing the exact area of your shower is essential. If you buy too few, you might run out before the job’s done. Buy too many, and you’ve spent extra money for no reason. Measuring it right from the start saves you both time and cash.
The Basic Formula
To find the square footage of your shower walls:
Square Feet = Length × Height (for each wall)
Then add up all the walls. Finally, adjust for waste. Here’s how it works.
Step-by-Step: Calculating Tiles for a Simple Shower
Let’s say your shower has three walls (the fourth is a glass door), and you’re tiling from floor to ceiling.
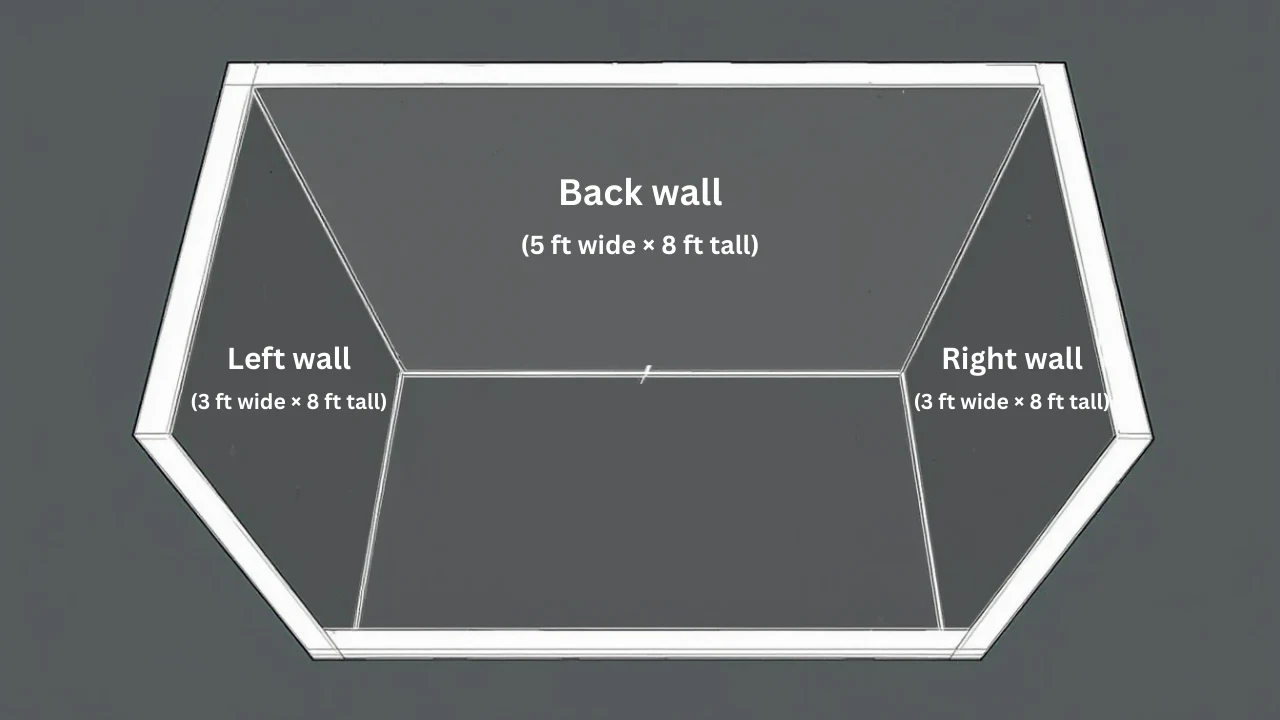
- Measure Each Wall: Use a tape measure.
- Wall 1 (back wall): 5 ft wide × 8 ft tall.
- Wall 2 (left wall): 3 ft wide × 8 ft tall.
- Wall 3 (right wall): 3 ft wide × 8 ft tall.
- Calculate Each Wall’s Area:
- Wall 1: 5 ft × 8 ft = 40 sq ft.
- Wall 2: 3 ft × 8 ft = 24 sq ft.
- Wall 3: 3 ft × 8 ft = 24 sq ft.
- Add Them Up:
- 40 sq ft + 24 sq ft + 24 sq ft = 88 sq ft.
Your shower walls total 88 square feet.
Adjusting for Openings and Niches
Showers often have areas you won’t tile, like a glass door, and extras like niches you will.
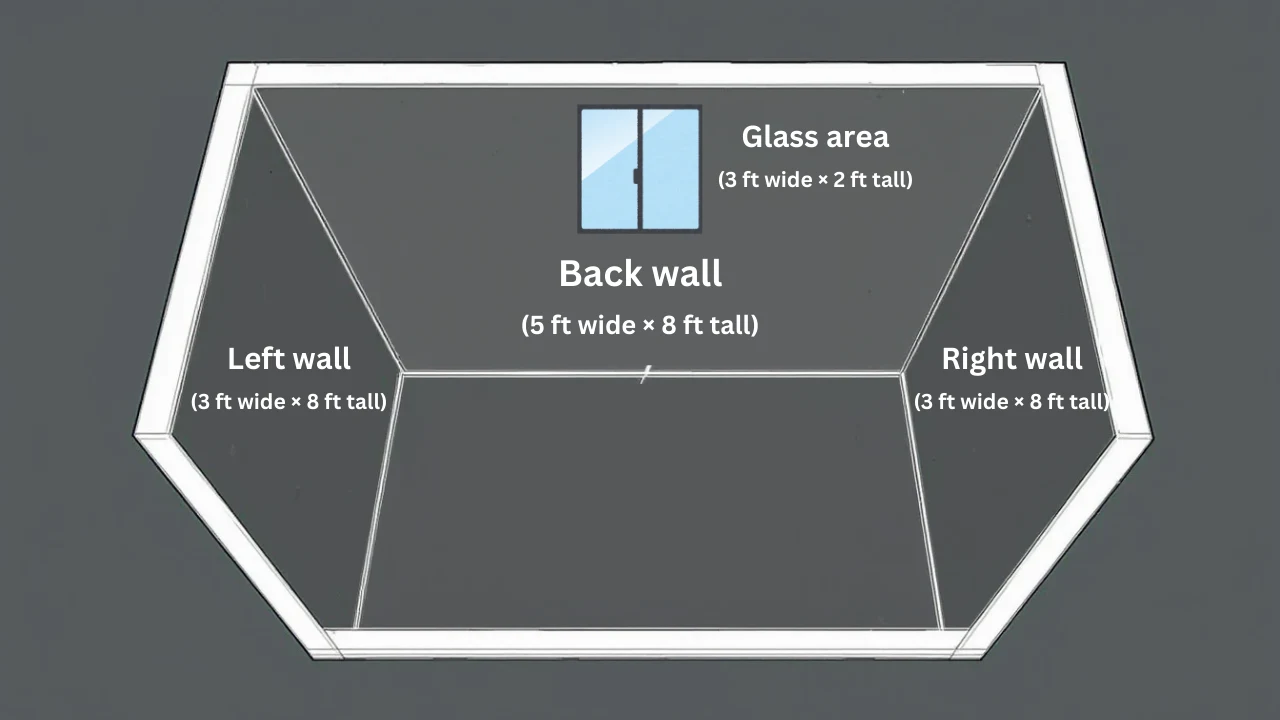
- Subtract Openings: If back wall has a glass section (say 3 ft × 2 ft at the top):
- Glass area: 3 ft × 2 ft = 6 sq ft.
- Back wall adjusted: 40 sq ft - 6 sq ft = 34 sq ft.
- New total: 34 + 24 + 24 = 82 sq ft.
- Add Niches: If there’s a niche on Wall 1 (1 ft × 1 ft, 0.5 ft deep):
- Niche back: 1 ft × 1 ft = 1 sq ft.
- Niche sides (two): 1 ft × 0.5 ft = 0.5 sq ft each = 1 sq ft total.
- Niche top/bottom (two): 1 ft × 0.5 ft = 0.5 sq ft each = 1 sq ft total.
- Total niche: 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 sq ft.
- New total: 82 sq ft + 3 sq ft = 85 sq ft.
Add Extra for Waste
Tiles break, cuts go wrong, and patterns need matching. Add 10-15% extra:
- 85 sq ft × 1.15 (15% extra) = 97.75 sq ft.
Round up to 98 sq ft. That’s how much tile you need to buy.
Pro Tips for Beginners
- Measure in Feet: If you get inches, convert them (12 inches = 1 ft, 6 inches = 0.5 ft).
- Tile Size Matters: If using 12x12 inch tiles (1 sq ft each), 98 sq ft = 98 tiles. For 6x6 inch tiles (4 per sq ft), you’d need 98 × 4 = 392 tiles.
- Double-Check: Measure twice to avoid mistakes.
- Shower Floor: If tiling the floor (e.g., 5 ft × 3 ft = 15 sq ft), add that to your total before waste.
Why This Matters
Getting the right tile amount saves you from last-minute store runs or overbuying. Plus, it’s a skill you can use for any tiling project—bathrooms, kitchens, you name it.
Wrap-Up
Measure each wall, multiply length by height, adjust for openings and niches, and add 15% for waste. That’s all it takes! Grab a tape measure and try it on your shower—you’ll be tiling like a pro in no time.
Recent Posts
How Much Rebar Do I Need? – A Complete Guide
How Much Epoxy Do You Need for Your Floor?
How to Calculate Yards of Concrete: A Simple Guide for Your Next Project
Difference Between Cement and Concrete: What You Need to Know
Roof Truss: Picking the Right Thickness for Your Project
Concrete Slab Construction: Materials, Process & Thickness Rules
How to Calculate Square Feet of a Wall: A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide
What is Crown Molding? Its Pros, Cons, and Uses
What is MDF? A Complete Guide to Medium-Density Fiberboard
What is Concrete? History, Types, Costs, and Tips for Working with It
What is Asphalt, How is it Made, and How Much Does it Cost?
Drywall: A Complete Guide to Installation, Repair, and Finishing
Floor Wax Guide: Best Practices for Wood, Tile, and Hardwood Surfaces
Tar and Gravel Roofs: A Durable Roofing Solution for Modern Homes
What Masonry Sand Is and Its Uses
Building and Installing Post and Rail Fences
Best Plywood Types for Roofing: Strength, Durability, and Protection
Slope: Why It Matters and How to Define It
Roof Panels: Types, Installation, Costs, and Maintenance
Electric Fences: Installation, Costs, Testing, and How They Work
How to Calculate Acreage of an Irregular Lot?
How Deep Should a Patio Base Be? Expert Tips and Material Choices
Deck Posts: Types, Materials, Pros & Cons, and Spacing
Types of Stone Wall: A Complete Guide
Mild Steel vs Carbon Steel | What is the differance?
How Deep Should a Fence Post Be?
5052 vs. 6061 Aluminum: Key Differences and Best Uses
Carpet Area vs Built-Up Area: What’s the Difference and How to Calculate?